Understanding Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) in children
SMA is an autosomal recessive hereditary disease characterized by progressive hypotonia and muscular weakness.The characteristic muscular weakness occur due to progressive degeneration of alpha motor neuron from anterior horn cells of spinal cord.
The weaknesses is more severe in proximal muscles than in distal segments.In some patients motor neuron of cranial nerves can also be involved.Several muscles are spared including diaphragm, involuntary muscles of GIT system, heart and sphincters. SMA is most common diagnosis in girls with progressive weakness and it is one of the most common genetic cause of death in children.
Causes :
SMA is usually inherited i.e both parents must have an altered gene or a missing copy of the gene involved in disorder. Most cases are caused by deficiency of a specific protein called SMN that is 'survival of motor neuron'. If a child receive the mutated SMN gene from only one parent then the child will be a SMA career, which means that the child will not show any sign of having a disease but it may have the probability that his own child will be affected.
Some patients with SMA have a homozygous deletion of telomeric s m n 1 gene found in the arm 5 t q.This deletion is demonstrated in up to 98 % of patients with SMA. The absence or dysfunction of SMA is reflected by enhanced neuronal death. A heterozygous deletion leads to an asymptomatic carrier state. a significant increase in nuclear DNA vulnerability was detected in fetus with s m a at 12 to 15 weeks gestational age. it reflected a decrease in number of anterior horn neurons. this vulnerability is no longer seen in rest of prenatal or postnatal period. abnormal cell morphology was seen only in post natal period.
Classification :
Different types of SMA are genetically similar but differ in presentation and in their clinical course.
Physical findings for each type of SMA are as follows
type 1
-newborn with type 1 are floppy and inactive
-moves extremities very little
-hips are flexed, abducted, externally rotated and knees in flexion
-because the distal muscle is usually spared, fingers and toes move.
-infants cannot control on lift head
-areflexia is universal
type 2
-patient have head control
-75 % of these patients sit independently
-muscle weakness is greater in lower extremity pain than in upper extremity
-patellar reflex is absent
-tongue fasiculations are present
-scoliosis is universal and most patients develop hip dislocation
type 3
-these patients work early in life and maintain their ambulatory capacity in to adolescence
-weakness may cause foot drop
-patient has limited endurance and will be wheelchair bound as adults
Diagnosis :
The diagnosis is based upon several test such as Nerve Conduction Test, CT Scan, MRI, muscle tissue biopsy along with gene testing.
Babies with SMA will have difficulty in crawling, walking and sometimes in breathing; as a child grows older he/she might have problem in getting around and requires assistance in basic activities of daily living feeding an combing.
Treatment of SMA :
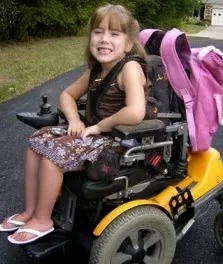 The goal of treatment is to relieve maintain function and improve child's mobility along with maximizing his independence and quality of life.
The goal of treatment is to relieve maintain function and improve child's mobility along with maximizing his independence and quality of life.
In case of spinal deformities, children will be given splint, brace, or corset to straighten their backs as toddlers or adolescents. Sometimes, surgery such as a spinal fusion is done to correct the spinal deformity in children.
As the the muscles for chewing, sucking, and swallowing are also affected, the child will become malnourished or develop pneumonia. Some children do better by eating small, frequent meals throughout the day instead of having three large meals.
Gastrotomy tube is given to those children who can't swallow or suck , through which they can receive a nutritionally sound liquid diet.
 |
| spinal muscular atrophy |
SMA is an autosomal recessive hereditary disease characterized by progressive hypotonia and muscular weakness.The characteristic muscular weakness occur due to progressive degeneration of alpha motor neuron from anterior horn cells of spinal cord.
The weaknesses is more severe in proximal muscles than in distal segments.In some patients motor neuron of cranial nerves can also be involved.Several muscles are spared including diaphragm, involuntary muscles of GIT system, heart and sphincters. SMA is most common diagnosis in girls with progressive weakness and it is one of the most common genetic cause of death in children.
Causes :
SMA is usually inherited i.e both parents must have an altered gene or a missing copy of the gene involved in disorder. Most cases are caused by deficiency of a specific protein called SMN that is 'survival of motor neuron'. If a child receive the mutated SMN gene from only one parent then the child will be a SMA career, which means that the child will not show any sign of having a disease but it may have the probability that his own child will be affected.
Some patients with SMA have a homozygous deletion of telomeric s m n 1 gene found in the arm 5 t q.This deletion is demonstrated in up to 98 % of patients with SMA. The absence or dysfunction of SMA is reflected by enhanced neuronal death. A heterozygous deletion leads to an asymptomatic carrier state. a significant increase in nuclear DNA vulnerability was detected in fetus with s m a at 12 to 15 weeks gestational age. it reflected a decrease in number of anterior horn neurons. this vulnerability is no longer seen in rest of prenatal or postnatal period. abnormal cell morphology was seen only in post natal period.
Classification :
Different types of SMA are genetically similar but differ in presentation and in their clinical course.
Physical findings for each type of SMA are as follows
type 1
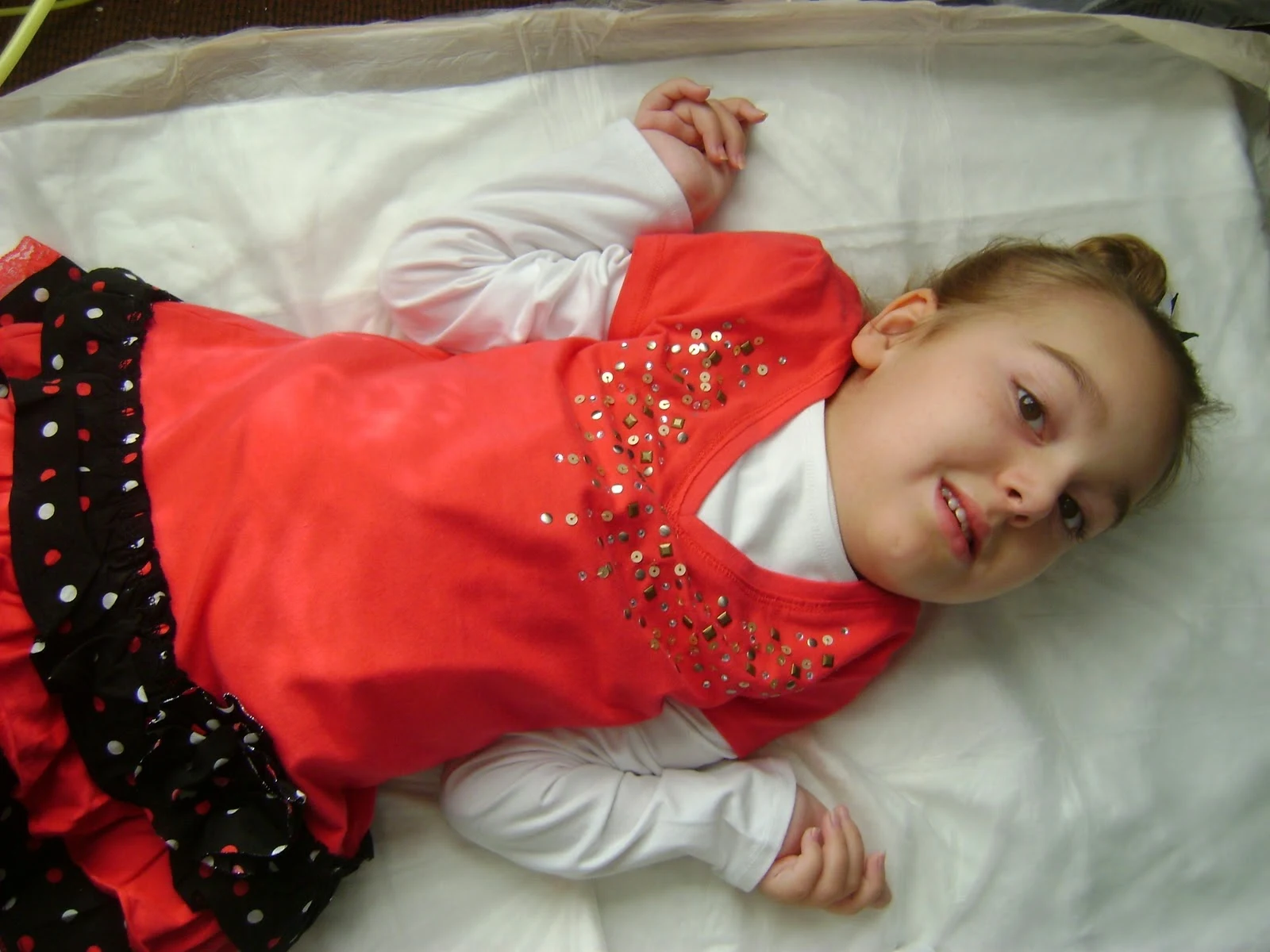 |
| typical position of child |
-moves extremities very little
-hips are flexed, abducted, externally rotated and knees in flexion
-because the distal muscle is usually spared, fingers and toes move.
-infants cannot control on lift head
-areflexia is universal
type 2
-patient have head control
-75 % of these patients sit independently
-muscle weakness is greater in lower extremity pain than in upper extremity
-patellar reflex is absent
-tongue fasiculations are present
-scoliosis is universal and most patients develop hip dislocation
type 3
-these patients work early in life and maintain their ambulatory capacity in to adolescence
-weakness may cause foot drop
-patient has limited endurance and will be wheelchair bound as adults
Diagnosis :
The diagnosis is based upon several test such as Nerve Conduction Test, CT Scan, MRI, muscle tissue biopsy along with gene testing.
Babies with SMA will have difficulty in crawling, walking and sometimes in breathing; as a child grows older he/she might have problem in getting around and requires assistance in basic activities of daily living feeding an combing.
Treatment of SMA :
 The goal of treatment is to relieve maintain function and improve child's mobility along with maximizing his independence and quality of life.
The goal of treatment is to relieve maintain function and improve child's mobility along with maximizing his independence and quality of life.In case of spinal deformities, children will be given splint, brace, or corset to straighten their backs as toddlers or adolescents. Sometimes, surgery such as a spinal fusion is done to correct the spinal deformity in children.
As the the muscles for chewing, sucking, and swallowing are also affected, the child will become malnourished or develop pneumonia. Some children do better by eating small, frequent meals throughout the day instead of having three large meals.
Gastrotomy tube is given to those children who can't swallow or suck , through which they can receive a nutritionally sound liquid diet.
Comments
Post a Comment